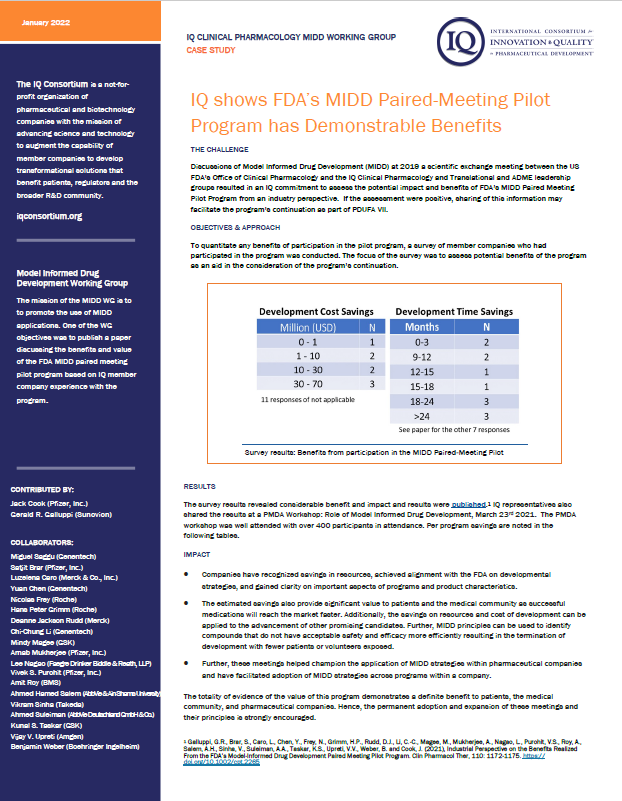
IQ Consortium Case StudiesIQ Shows FDA's MIDD Paired-Meeting Pilot Program has Demonstrable BenefitsDiscussions of Model Informed Drug Development (MIDD) at 2019 a scientific exchange meeting between the US FDA’s Office of Clinical Pharmacology and the IQ Clinical Pharmacology and Translational and ADME leadership groups resulted in an IQ commitment to assess the potential impact and benefits of FDA’s MIDD Paired Meeting Pilot Program from an industry perspective. If the assessment were positive, sharing of this information may facilitate the program’s continuation as part of PDUFA VII. Subvisible ParticlesSubvisible particles (SVP, 2-100 µm) and submicron particles (SMP, 0.1-2 µm) in therapeutic protein products are topics of high interest for drug product developers and regulators due to their potential to elicit an immunogenic response that may affect drug safety and efficacy. Currently, there is no clear guidance on how and when to measure SMP. Limited information is available on the level of SMP in clinical and commercial products. Although SMP instruments are available, the robustness and performance of these detection methods and their proper use for routine characterization of clinical and commercial products still needs to be explored in more detail. |
|
Extrapolation: A New Tool Making Pediatric Drug Development More FeasiblePediatric extrapolation utilizes and integrates available knowledge in adult populations (“priors”), and identifies critical gaps and uncertainties in that knowledge, to define a targeted set of required clinical data to fill the knowledge gaps for application to pediatric patients. Although the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA) and National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) have adopted the International Council for Harmonization (ICH) Guideline: E11 (R1) Addendum thereby encouraging extrapolation, good use cases were lacking and the full potential and application opportunities were not fully realized. In particular, questions of general applicability of pediatric extrapolation to a certain disease, disease similarity, and whether or not these are pertinent to the use of a new molecular entity in pediatric patients were sometimes the reason for controversial perceptions of industry, academia and even between regulatory bodies. |
|
Assessing the Value of Nonclinical Combination Toxicity Studies for Supporting Development of Combination ProductsOur case studies describe initiatives undertaken by IQ's Working Groups in detail, including the challenges they set out to address, their approaches, and the results and impact of their work.Interest in developing combination products to overcome drug resistance and treat complex diseases is growing. However, ambiguity remains around the value of combination toxicity studies to support combination products. A better understanding of current industry practices and rationale for nonclinical combination toxicity studies is needed. The IQ Nonclinical Safety Assessments to Support Development of Combination Products Working Group developed a survey to acquire this understanding. As the pharmaceutical industry’s experience with combination products grows, these data will be critical for determining how relevant the nonclinical combination toxicity studies are for informing clinical development of combination products. |
|
Assessing the Value of Nonclinical Testing to Enable Safe Entry to First in Human Clinical TrialsBefore a new drug can be evaluated in human clinical trials, study sponsors are required to conduct animal toxicology studies to understand potential toxic effects of the drug and help establish a starting clinical dose. This testing, which is required by regulatory agencies, assumes that the animal model and toxicology studies will identify possible human hazards. However, there is active debate in the literature about the utility of animal testing in drug development and there is limited published data that scientifically addresses correlations between toxicities observed in animal models to adverse events in humans. The IQ Nonclinical to Clinical Translational Safety Working Group addressed this gap in information by collecting and analyzing how animal toxicity data predicted safety issues in humans in studies. |
|
Advancing Global Collaboration in Pediatric Formulation DevelopmentThe use of pharmaceuticals for treatment of pediatric patients is ubiquitous in clinical practice. In many instances, clinicians, pharmacists, and parents treat children with dose forms and products designed for and tested in adults. This practice can lead to incorrect dosing, poor acceptance, and therapeutic failure or adverse events. Enhanced awareness of these issues, pediatric patients’ needs, and evolving regulatory expectations has generated a focus on development of age-appropriate pediatric drug products for clinical and commercial use. Understanding the best product presentations for a diverse pediatric population as well as how to administer these products and assess their acceptability are areas of key importance and rapid innovation for regulators, academics, and the pharmaceutical industry. The Drug Product Pediatric Working Group was created to address the above challenges and catalyze advancement of science and technologies for age-appropriate formulation development. |
|
Inspiring Sustainable Drug Manufacturing with a Smart Goal MetricGreen and sustainable chemistry is critical for balancing the long-term sustainability of business, society, and the environment. It stimulates scientific innovation, reduces environmental footprint, lowers development and manufacturing costs, and can therefore contribute to the greater affordability of drugs for patients. However, the full potential of sustainable drug manufacturing has been inhibited by the absence of harmonized green chemistry metrics, inconsistent starting points for analysis, and the neglected complexities of the structurally diverse drugs and their manufacturing processes. The IQ Consortium’s Green Chemistry Working Group, the ACS Green Chemistry Institute Pharmaceutical Roundtable, and Professor Roger Sheldon joined efforts to create a green chemistry metric that could catalyze innovative green process chemistry, and create a platform to reward the greenest manufacturing process. |
|
Development of An IQ Assessment Tool to Streamline Review of Contracted Animal Research ProgramsWithin the last 20 years, pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies have increasingly outsourced animal studies to contract research organizations. With this shift, companies found that some programs, especially in developing countries, were not upholding the high standards for animal care and use expected by the biopharma industry. To address this, individual companies began creating programs and processes to standardize animal studies. This resulted in an increasingly burdensome workload for contract research programs that must complete a large number of different animal program assessment questionnaires to meet the expectations of individual companies. The objective of this project was to find a way to help ensure that CROs meet high animal care standards while reducing the burden associated with completing many different company questionnaires. |
|